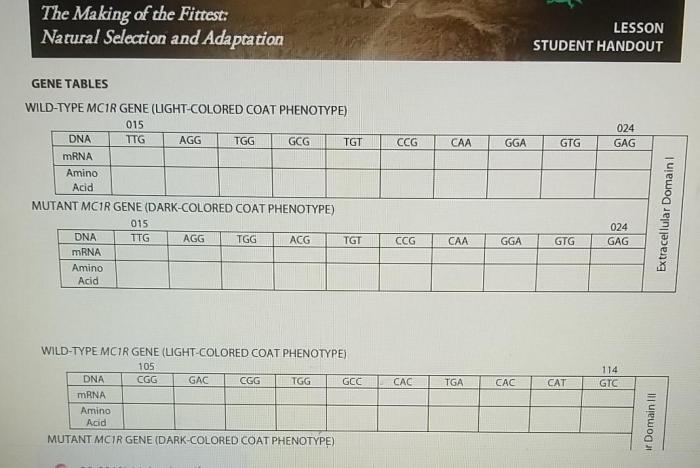
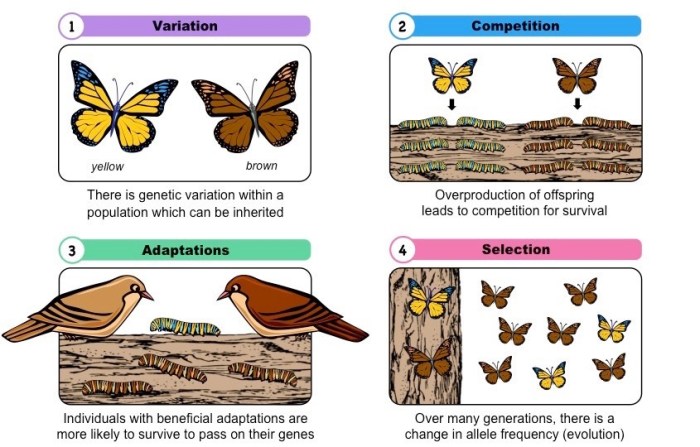
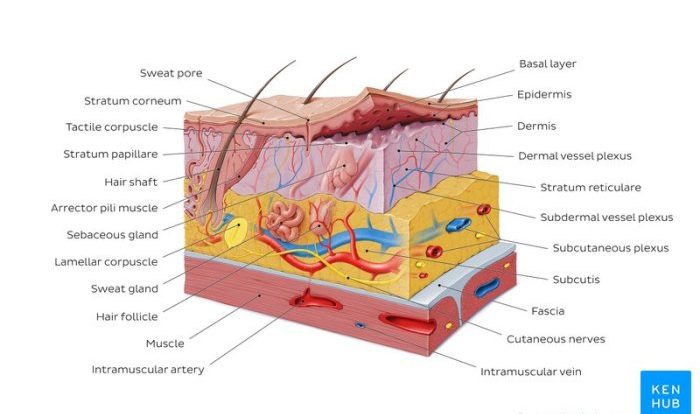
The making of the fittest: natural selection answer key sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Natural selection, a cornerstone of evolutionary theory, serves as the driving force behind the remarkable diversity of life on Earth. This concept, proposed by Charles Darwin, elucidates the mechanisms by which organisms adapt to their environment, leading to the survival and proliferation of the fittest individuals.
Introduction to Natural Selection

Natural selection is a fundamental mechanism of evolution that drives the adaptation of species to their environment. It explains how organisms with traits that enhance their survival and reproduction tend to produce more offspring, passing on those advantageous traits to subsequent generations.
Key principles of natural selection include:
- Variation:Individuals within a population exhibit genetic diversity, resulting in phenotypic variation.
- Inheritance:Traits are passed down from parents to offspring through genetic material.
- Differential Survival and Reproduction:Individuals with traits that provide an advantage in their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Mechanisms of Natural Selection
Variation arises through mutations, genetic recombination, and other mechanisms that introduce genetic diversity into a population.
Types of selection include:
- Directional Selection:Favors one extreme of a trait, shifting the population mean in that direction.
- Stabilizing Selection:Favors an intermediate trait value, maintaining the status quo.
- Disruptive Selection:Favors both extremes of a trait, leading to the evolution of distinct subpopulations.
Natural selection can result in adaptations, which are traits that enhance an organism’s fitness in a particular environment.
Evidence for Natural Selection, The making of the fittest: natural selection answer key
The fossil record provides evidence of evolutionary changes over time, supporting the theory of natural selection.
Comparative anatomy and molecular biology reveal homologous structures and shared genetic sequences, indicating common ancestry and the influence of natural selection.
Ongoing natural selection is observed in modern populations, such as the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
The Making of the Fittest
Natural selection leads to the “survival of the fittest” by favoring individuals with traits that enhance their fitness.
Fitness is a measure of an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce in a given environment.
Natural selection has shaped the diversity of life on Earth, from the emergence of complex organisms to the adaptation of species to changing environments.
Limitations of Natural Selection
Natural selection depends on the availability of genetic variation and can be constrained by genetic drift.
Natural selection can lead to maladaptations or extinction if environmental changes outpace the rate of adaptation.
In some cases, other evolutionary forces, such as genetic drift or sexual selection, may play a more significant role than natural selection.
Applications of Natural Selection
Natural selection has applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and conservation.
In medicine, understanding natural selection can aid in the development of new drugs and therapies.
In agriculture, natural selection is used to improve crop yields and develop pest-resistant varieties.
In conservation, natural selection can inform strategies for protecting endangered species and preserving biodiversity.
Common Queries: The Making Of The Fittest: Natural Selection Answer Key
What is natural selection?
Natural selection is a fundamental mechanism of evolution that favors the survival and reproduction of individuals with traits that enhance their adaptation to their environment.
How does natural selection lead to the survival of the fittest?
Natural selection operates on the principle of differential survival and reproduction. Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and pass on their genes, leading to the gradual accumulation of favorable traits within a population.
What are the limitations of natural selection?
Natural selection is constrained by the availability of genetic variation and can be influenced by random genetic drift. Additionally, natural selection may not always lead to optimal outcomes and can result in maladaptations or extinction.