Dna replication worksheet answers pdf – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of DNA replication with our comprehensive worksheet answers PDF. This meticulously crafted guide empowers you to decipher the intricate mechanisms of cell division, unlocking the secrets of genetic inheritance and the remarkable applications of biotechnology.
Delve into the fascinating world of DNA replication, exploring the role of enzymes, the stages of initiation, elongation, and termination, and the significance of leading and lagging strands. Gain insights into the potential errors that can arise during replication and their implications for genetic stability.
Introduction
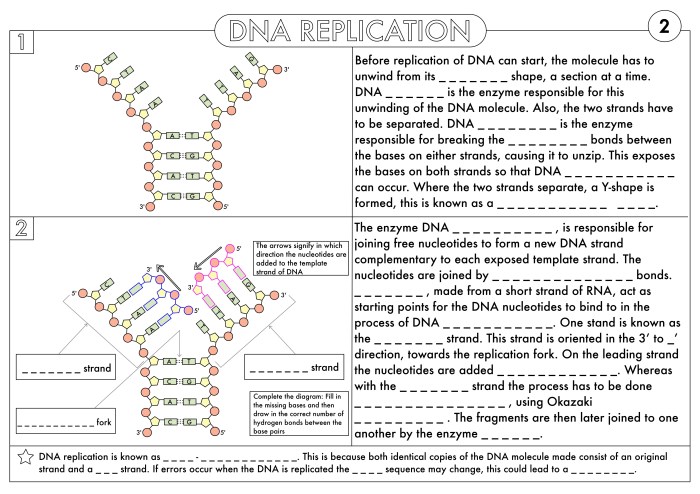
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It is essential for cell division, as each new cell must have its own copy of the DNA. The process of DNA replication is carried out by a number of enzymes, including DNA polymerase, which adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, and helicase, which unwinds the DNA double helix.
Role of Enzymes in DNA Replication
Enzymes play a vital role in DNA replication. DNA polymerase is the main enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands. It adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand in a 5′ to 3′ direction. Helicase is another important enzyme involved in DNA replication.
It unwinds the DNA double helix, allowing DNA polymerase to access the template strand. Other enzymes involved in DNA replication include primase, which synthesizes the RNA primers that are required for DNA polymerase to start synthesis, and ligase, which joins the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
Steps of DNA Replication
DNA replication is a fundamental biological process that ensures the accurate duplication of genetic information during cell division. It involves three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.
Initiation
Initiation of DNA replication occurs at specific regions called origins of replication (ORIs). Here, the enzyme helicase unwinds the DNA double helix, breaking the hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs. This creates a replication bubble with two replication forks, each consisting of a leading strand and a lagging strand.
Elongation
Elongation is the continuous synthesis of new DNA strands by the enzyme DNA polymerase. On the leading strand, DNA polymerase can continuously add nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing strand, following the template strand. On the lagging strand, DNA polymerase must synthesize short fragments of DNA called Okazaki fragments in the 5′ to 3′ direction, away from the replication fork.
These fragments are later joined together by the enzyme DNA ligase.
Termination
Termination of DNA replication occurs when the replication forks reach the end of the chromosome. On linear chromosomes, special structures called telomeres prevent the loss of genetic information during replication. On circular chromosomes, the replication forks meet at a specific termination site.
DNA Replication Errors: Dna Replication Worksheet Answers Pdf
DNA replication errors occur during the DNA replication process, which is essential for cell division and growth. These errors can lead to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence that can have a variety of effects on the cell.
There are three main types of DNA replication errors:
- Base substitution errorsoccur when one base is replaced by another base.
- Insertion errorsoccur when an extra base is added to the DNA sequence.
- Deletion errorsoccur when a base is removed from the DNA sequence.
DNA replication errors can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- DNA polymerase errors: DNA polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands. Errors can occur when DNA polymerase inserts the wrong base into the new strand.
- Nucleotide pool imbalances: If the nucleotide pool is imbalanced, it can lead to the incorporation of incorrect bases into the new DNA strand.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors, such as radiation and chemicals, can damage DNA and lead to replication errors.
DNA replication errors can have a variety of effects on the cell. Some errors may be harmless, while others may lead to mutations. Mutations can have a range of effects on the cell, including:
- Silent mutations: Silent mutations do not change the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene.
- Missense mutations: Missense mutations change the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene.
- Nonsense mutations: Nonsense mutations introduce a stop codon into the gene, which can lead to the production of a truncated protein.
- Frameshift mutations: Frameshift mutations insert or delete a base from the gene, which can shift the reading frame of the gene and lead to the production of a non-functional protein.
DNA replication errors are a major source of genetic variation. Genetic variation is essential for evolution, as it allows for the development of new traits and the adaptation of populations to new environments.
Applications of DNA Replication
DNA replication plays a crucial role in various biotechnological applications and genetic engineering techniques. It enables the manipulation and amplification of specific DNA sequences, facilitating advancements in medical research, diagnostics, and industrial processes.
Biotechnology
In biotechnology, DNA replication forms the foundation of several key techniques:
- Gene Cloning:DNA replication is employed to amplify specific genes or DNA fragments using techniques like polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This allows researchers to obtain multiple copies of the target DNA for further analysis or genetic manipulation.
- DNA Sequencing:DNA replication is essential for DNA sequencing methods like Sanger sequencing and next-generation sequencing. It generates multiple copies of the target DNA, allowing the determination of the nucleotide sequence.
- DNA Fingerprinting:DNA replication enables the creation of DNA fingerprints, which are unique patterns used for identification purposes in forensic science, paternity testing, and genetic research.
Genetic Engineering
In genetic engineering, DNA replication is pivotal for:
- Genetic Modification:DNA replication is employed to introduce specific changes into DNA sequences, such as gene insertion, deletion, or modification. This enables the creation of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) with desired traits.
- Gene Therapy:DNA replication is crucial for the development of gene therapies that aim to treat genetic disorders by introducing functional genes into patients’ cells.
- Synthetic Biology:DNA replication is used to assemble and create artificial DNA constructs for various applications, such as the development of biosensors and biofuels.
DNA Replication Worksheet

DNA replication is a fundamental process in biology that ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of DNA replication, including its steps, errors, applications, and key concepts.
DNA Replication Worksheet
This worksheet consists of a series of questions and exercises designed to test your understanding of DNA replication. It covers various aspects of the process, including the enzymes involved, the different stages of replication, and the mechanisms that ensure accuracy and fidelity.
The worksheet also includes a table summarizing the key concepts of DNA replication, providing a concise overview of the process and its significance.
Key Concepts of DNA Replication
- DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, meaning that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- The process is carried out by a complex of enzymes, including DNA polymerase, helicase, and ligase.
- Replication occurs in three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.
- Errors during replication can lead to mutations, which can have a variety of effects on the organism.
- DNA replication is essential for cell division and growth, as well as for the transmission of genetic information to offspring.
DNA Replication Quiz

This quiz will assess your understanding of the process of DNA replication. Answer all questions to the best of your ability.
Multiple Choice, Dna replication worksheet answers pdf
- Which enzyme is responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during replication?
- Helicase
- Polymerase
- Ligase
- Primase
- What is the role of the primer in DNA replication?
- To initiate DNA synthesis by providing a 3′ hydroxyl group
- To terminate DNA synthesis
- To proofread the newly synthesized DNA strand
- To unwind the DNA double helix
- Which of the following is NOT a feature of DNA replication?
- Semi-conservative
- Bidirectional
- Catalyzed by RNA polymerase
- Requires energy in the form of ATP
True/False
- DNA replication occurs only during the S phase of the cell cycle.
- Leading and lagging strands are synthesized in the same direction.
- Okazaki fragments are joined together by ligase.
- DNA polymerase can add nucleotides to both the 3′ and 5′ ends of a DNA strand.
Short Answer
- Explain the role of telomerase in DNA replication.
- Describe the process of DNA replication in prokaryotic cells.
- Discuss the importance of DNA replication in living organisms.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information during cell division, enabling the growth and repair of tissues.
How do enzymes contribute to DNA replication?
Enzymes such as DNA polymerase and helicase play crucial roles in unwinding the DNA double helix, synthesizing new strands, and proofreading for errors.
What are the potential consequences of DNA replication errors?
Errors in DNA replication can lead to mutations, which may have implications for genetic disorders, cancer development, and aging.